The Great Québec Blackout
March 13, 2021: They call it “the day the sun brought darkness.” On March 13, 1989, a powerful coronal mass ejection (CME) hit Earth’s magnetic field. Ninety seconds later, the Hydro-Québec power grid failed. During the 9 hour blackout that followed, millions of Quebecois found themselves with no light or heat, wondering what was going on?
“It was the biggest geomagnetic storm of the Space Age,” says Dr. David Boteler, head of the Space Weather Group at Natural Resources Canada. “March 1989 has become the archetypal disturbance for understanding how solar activity can cause blackouts.”

It seems hard to believe now, but in 1989 few people realized solar storms could bring down power grids. The warning bells had been ringing for more than a century, though. In Sept. 1859, a similar CME hit Earth’s magnetic field–the infamous “Carrington Event“–sparking a storm twice as strong as March 1989. Electrical currents surged through Victorian-era telegraph wires, in some cases causing sparks and setting telegraph offices on fire. These were the same kind of currents that would bring down Hydro-Québec.
“The March 1989 blackout was a wake-up call for our industry,” says Dr. Emanuel Bernabeu of PJM, a regional utility that coordinates the flow of electricity in 13 US states. “Now we take geomagnetically induced currents (GICs) very seriously.”
What are GICs? Freshman physics 101: When a magnetic field swings back and forth, electricity flows through conductors in the area. It’s called “magnetic induction.” Geomagnetic storms do this to Earth itself. The rock and soil of our planet can conduct electricity. So when a CME rattles Earth’s magnetic field, currents flow through the soil beneath our feet.

Québec is especially vulnerable. The province sits on an expanse of Precambrian igneous rock that does a poor job conducting electricity. When the March 13th CME arrived, storm currents found a more attractive path in the high-voltage transmission lines of Hydro-Québec. Unusual frequencies (harmonics) began to flow through the lines, transformers overheated and circuit breakers tripped.
After darkness engulfed Quebec, bright auroras spread as far south as Florida, Texas, and Cuba. Reportedly, some onlookers thought they were witnessing a nuclear exchange. Others thought it had something to do with the space shuttle (STS-29), which remarkably launched on the same day. The astronauts were okay, although the shuttle did experience a mysterious problem with a fuel cell sensor that threatened to cut the mission short. NASA has never officially linked the sensor anomaly to the solar storm.
Much is still unknown about the March 1989 event. It occurred long before modern satellites were monitoring the sun 24/7. To piece together what happened, Boteler has sifted through old records of radio emissions, magnetograms, and other 80s-era data sources. He recently published a paper in the research journal Space Weather summarizing his findings — including a surprise:
“There were not one, but two CMEs,” he says.
The sunspot that hurled the CMEs toward Earth, region 5395, was one of the most active sunspot groups ever observed. In the days around the Quebec blackout it produced more than a dozen M- and X-class solar flares. Two of the explosions (an X4.5 on March 10th and an M7.3 on March 12th) targeted Earth with CMEs.
“The first CME cleared a path for the second CME, allowing it to strike with unusual force,” says Boteler. “The lights in Québec went out just minutes after it arrived.”

Among space weather researchers, there has been a dawning awareness in recent years that great geomagnetic storms such as the Carrington Event of 1859 and The Great Railroad Storm of May 1921 are associated with double (or multiple) CMEs, one clearing the path for another. Boteler’s detective work shows that this is the case for March 1989 as well.
The March 1989 event kicked off a flurry of conferences and engineering studies designed to fortify grids. Emanuel Bernabeu’s job at PJM is largely a result of that “Québec epiphany.” He works to protect power grids from space weather — and he has some good news.
“We have made lots of progress,” he says. “In fact, if the 1989 storm happened again today, I believe Québec would not lose power. The modern grid is designed to withstand an extreme 1-in-100 year geomagnetic event. To put that in perspective, March 1989 was only a 1-in-40 or 50 year event–well within our design specs.”
Some of the improvements have come about by hardening equipment. For instance, Bernabeu says, “Utilities have upgraded their protection and control devices making them immune to type of harmonics that brought down Hydro-Québec. Some utilities have also installed series capacitor compensation, which blocks the flow of GICs.”
Other improvements involve operational awareness. “We receive NOAA’s space weather forecast in our control room, so we know when a storm is coming,” he says. “For severe storms, we declare ‘conservative operations.’ In a nutshell, this is a way for us to posture the system to better handle the effects of geomagnetic activity. For instance, operators can limit large power transfers across critical corridors, cancel outages of critical equipment and so on.”
The next Québec-level storm is just a matter of time. In fact, we could be overdue. But, if Bernabeu is correct, the sun won’t bring darkness, only light.
👇👇👇👇TODAY:
CME IMPACT: A CME struck Earth today, July 25th, at 1422 UT. We're not sure, but this could be the halo CME launched toward Earth by a dark plasma eruption on July 21st. G1-class geomagnetic storms are possible in the hours ahead as Earth moves through the CME's magnetized wake. CME impact alerts: SMS Text
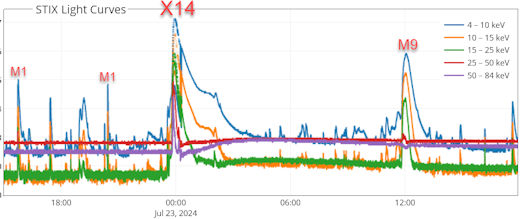
MAJOR FARSIDE SOLAR FLARE: The biggest flare of Solar Cycle 25 just exploded from the farside of the sun. X-ray detectors on Europe's Solar Orbiter (SolO) spacecraft registered an X14 category blast:
Solar Orbiter was over the farside of the sun when the explosion occured on July 23rd, in perfect position to observe a flare otherwise invisible from Earth.
"From the estimated GOES class, it was the largest flare so far," says Samuel Krucker of UC Berkeley. Krucker is the principal investigator for STIX, an X-ray telescope on SolO which can detect solar flares and classify them on the same scale as NOAA's GOES satellites. "Other large flares we've detected are from May 20, 2024 (X12) and July 17, 2023 (X10). All of these have come from the back side of the sun."
Meanwhile on the Earthside of the sun, the largest flare so far registered X8.9 on May 14, 2024. SolO has detected at least three larger farside explosions, which means our planet has been dodging a lot of bullets.
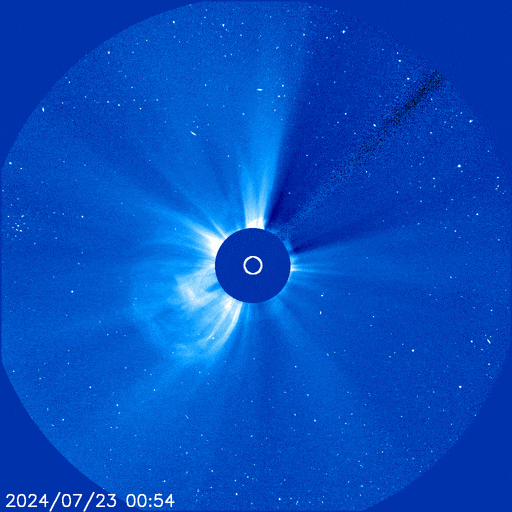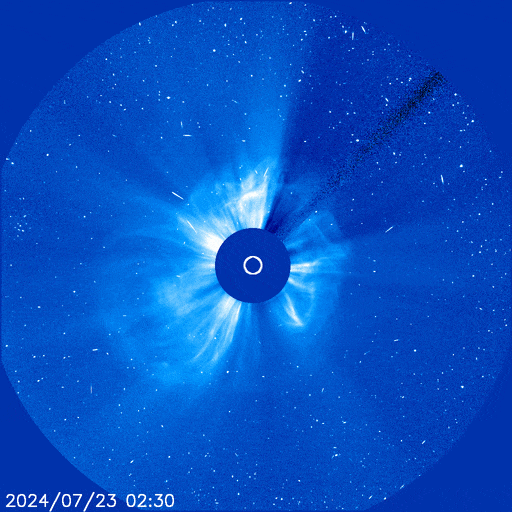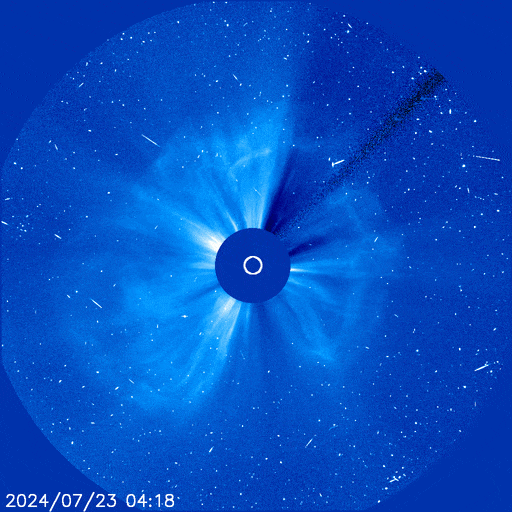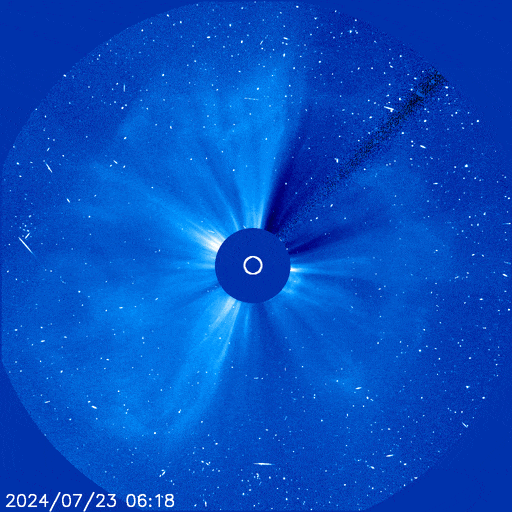
The X14 farside flare was indeed a major event. It hurled a massive CME into space, shown here in a coronagraph movie from the Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO):
The CME sprayed energetic particles all over the solar system. Earth itself was hit by 'hard' protons (E > 100 MeV) despite being on the opposite side of the sun.
"This is a big one--a 360 degree event," says George Ho of the Southwest Research Institute, principal investigator for one of the energetic particle detectors onboard SolO. "It also caused a high dosage at Mars."
SolO was squarely in the crosshairs of the CME, and on July 24th it experienced a direct hit. In a matter of minutes, particle counts jumped almost a thousand-fold as the spacecraft was peppered by a hail storm energetic ions and electrons.
"This is something we call an 'Energetic Storm Particle' (ESP) event," explains Ho. "It's when particles are locally accelerated in the CME's shock front [to energies higher than a typical solar radiation storm]. An ESP event around Earth in March 1989 caused the Great Quebec Blackout."
So that's what might have happened if the CME hit Earth instead of SolO. Maybe next time. The source of this blast will rotate around to face our planet a week to 10 days from now, so stay tuned. Solar flare alerts: SMS Text





.jpg)
.jpg)











